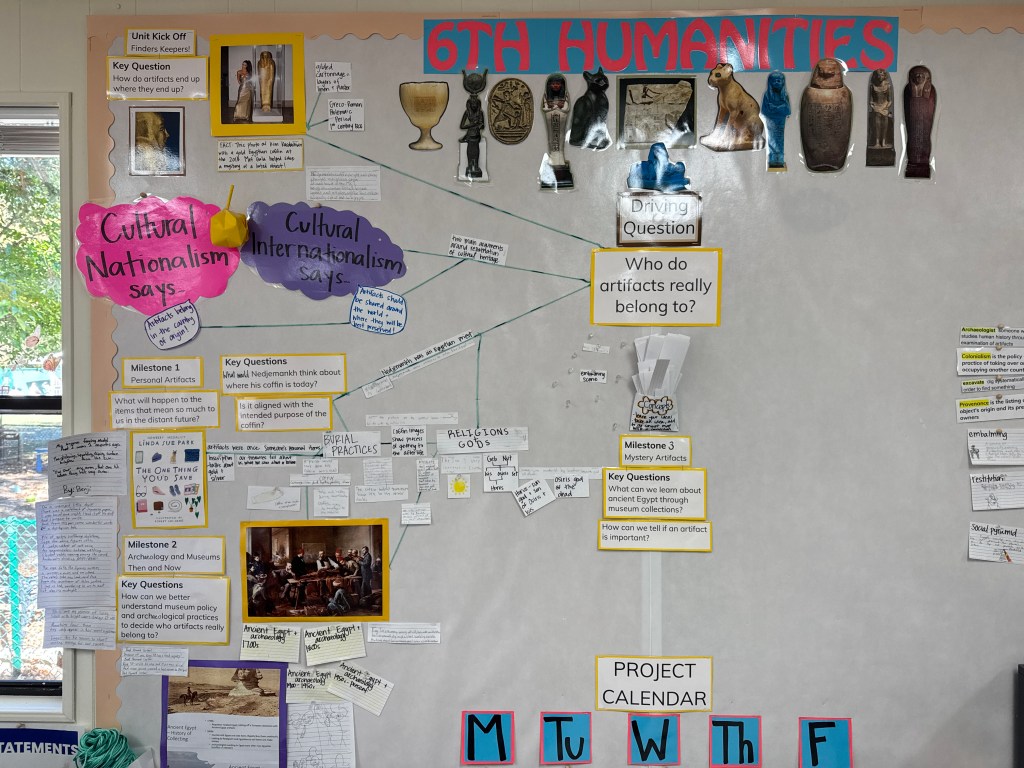
Sixth graders have begun their first PBL unit of the year, in which they seek to answer the driving question: Who do artifacts really belong to? During this unit, students will develop an understanding of what cultural heritage is, how artifacts tell the stories of people’s lives, the role of museums, the history of changing archaeological practices, ancient Egyptian civilization, history research skills, as well as sijo poetry, narrative, expository, and argumentative writing.
Recently, they’ve been thinking about the purpose of ancient artifacts, such as Nedjemankh’s stolen gold coffin, and about their connections to their own treasured possessions. The class read The One Thing You’d Save, by Linda Sue Park, before writing personal narratives about their own treasured artifacts. Students got lots of practice giving and receiving both teacher and peer critique on these pieces before turning in their final drafts.
Last week, they zoomed with an archaeologist, Dr. Hannah Wellman. She shared the evolution of ancient mummification practices, as well as changes in legal practices and ethical arguments regarding the treatment of ancient Egyptian cultural heritage. Dr. Wellman’s example of Nefertiti’s Bust as an example of the significance of museum context of artifacts gave the class a great launching point for discussions in preparation for visiting the Badè Museum this week.
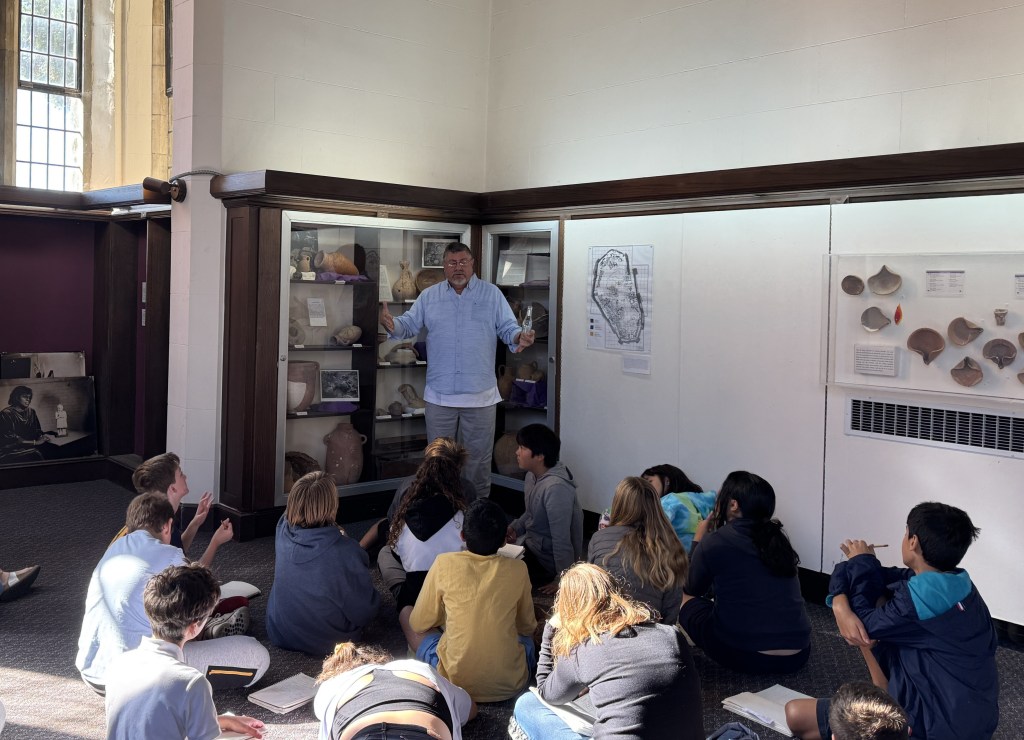
Dr. Aaron Brody, an archaeologist and Badè Museum director, taught the sixth graders about their collection, the benefits of a high degree of context for artifacts, and why repatriation in this case may not be ideal or desired for the museum or the country of origin. Both experts helped the class understand how repatriation conflicts came to be and why people have reached different conclusions about repatriation in various situations.
#SaklanPBL